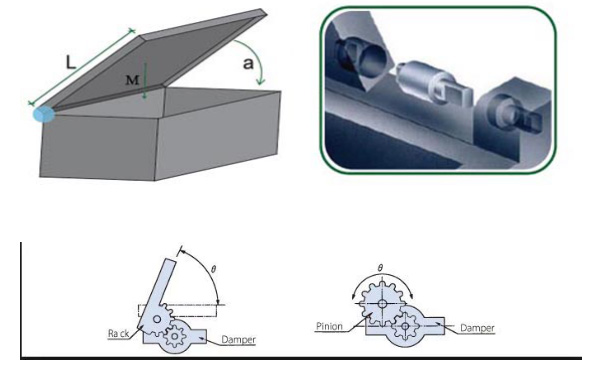
Damper Selection Recommendations
A. The cover plate falls freely and slowly (the rotating shaft is directly connected with the buffer shaft or the inner hole, as shown in the following figure). The cover plate falls slowly from less than 90 to 0 horizontally. The torque force of the cover plate acting on the rotating shaft
is calculated as follows: T = L/2 ×M × 9.8(N.m)
L: the size of the cover (m)
M: the weight of the cover (Kg)
spring force f, cover plate load w, and the relationship curve of the preselected damper torque t as shown in figure B below
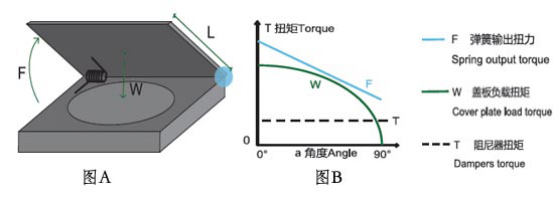
T<F-W
W: the cover plate load torque
requires the amount of torque that the spring supported cover plate or other mechanism acts on the rotating shaft.
F: Spring output torque
The spring force is sufficient to support the load resistance of the cover plate or other mechanism.
T: Damper torque
In order to ensure that the cover plate or other rotating mechanism can be smoothly rotated in place, the damper torque T should be slightly less than the difference between the spring output torque and the cover plate load torque.


